This article is more than 1 year old
P2P study: Music crackdown is bad for business
Music biz throwing away cash
A study of P2P music exchanges to be revealed this week suggests that the ailing music business is shunning a lucrative lifeline by refusing to license the activity for money.

Entitled "The Long Tail of P2P", the study by Will Page of performing rights society PRS For Music and Eric Garland of P2P research outfit Big Champagne will be aired at The Great Escape music convention tomorrow. It's a follow-up to Page's study last year which helped debunk the myth of the "Long Tail". Page examined song purchases at a large online digital retail store, which showed that out of an inventory of 13 million songs, 10 million had never been downloaded, even once. It suggested that the idea proposed by WiReD magazine editor Chris Anderson, who in 2004 urged that the future of business was digital retailers carrying larger inventories of slow-selling items was a Utopian fantasy.
The P2P networks are harder to quantify, but apparently show a similar pattern, where most of the action - and profit - is in the 'head'. Each Top 100 CD on on PirateBay averaged 58,000 downloads a week, for example. Lady GaGa's The Fame was downloaded 388,000 times in a week from PirateBay alone. Like its predecessor, the new study also finds that downloads follow a log-normal, rather a Pareto (or "power curve") distribution as Anderson envisaged. The WiReD man had guessed the shape of the internet - and picked the wrong shape.
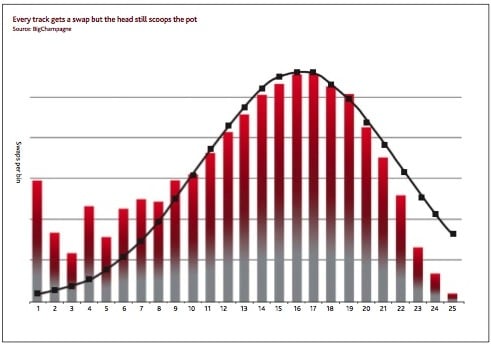
P2P swaps: where's the action?
The gap between bestsellers and the rest is widening, Page and Garland conclude, a pattern also seen with movie and TV consumption too. The authors cite one knock-on effect for live music promoters, who say bands fourth of fifth on a bill are relatively worse off than they were ten years ago. So much for the internet as the great leveller: You literally got lost in the noise.
But why does popular taste follow this shape?
For Andrew Bud, who worked on last year's study, the answer is simple:
"An obvious answer is that it’s through people chatting to each other and seeing the music talked about in the media. That’s what culture is. So the fact we’re seeing the log normal distribution here may point to the power of culture on people’s choices. Chris Anderson’s hypothesis of a Pareto power law would be much more about random, individual choices – people alone with their computers. So perhaps, this debate of 'thick versus fat' is really about the power of culture in determining demand".
Page says that once the nature of the digital market is understood, we can build businesses that reward composers and songwriters. (Not something a concern for the Pirates).
