This article is more than 1 year old
WTF is... DLNA?
A cure for media playback blues - or will it just have you seeing red?
How DLNA stacks up
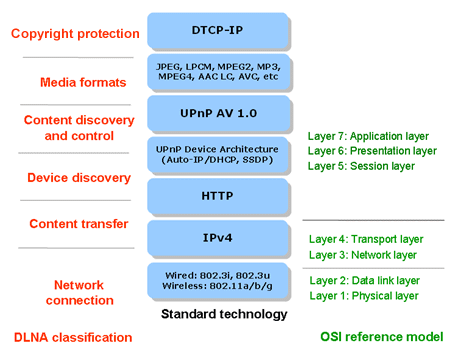
Device Discovery
The network layer is based on IP, either wired or wireless, and compatible devices discover each other using SSDP (Simple Service discovery Protocol), a fundamental of UPnP. This allows devices to reveal their names to one another, along with information about the functions they are capable of performing.
Content Discovery
UPnP is used between the connected devices to establish lists of the multimedia files available based on their associated metadata. DLNA guidelines dictate the mandatory formats - which include MPEG 2 and AVC/H.264 for video, PCM and AAC for audio, and JPG for pictures. Other formats - MP3 and Flac, for instance - are optional and may not necessarily be accepted by some DLNA-compliant devices.
Content Transfer
The devices exchange “media format profile IDs” to reach agreement about which files can be served and played. Content that passes the test is piped through the Web protocol HTTP. Premium content may be tagged using DTCP-IP “link protection” to ensure copyright material stays within defined bounds.