This article is more than 1 year old
Google caps punch-yourself-in-the-face malicious charger hack
Another reason to avoid those DEF CON charging stations.
Google has capped a dangerous but somewhat obscure boot mode vulnerability that allowed infected PCs and chargers to put top end Nexus phones into denial of service states.
IBM reported the flaw (CVE-2016-8467) which allows infected computers and malicious power chargers to compromise Nexus 6 and 6p phones.
Google badged the bug high severity and prevented locked bootloaders from booting into the necessary risky boot modes. Nexus 6 devices were patched in November while 6P devices received the update this month.
The vulnerability overcomes the normal requirement that phones already have adb enabled in developer options.
However, users in physical control of handsets will need to tap a prompt to authorise adb connectivity with the infected PC or charger for the attacks to work.
That is a function familar with those used to modifying their devices to install custom ROMs, something even security-minded individuals practice, and less so to users running stock phones.
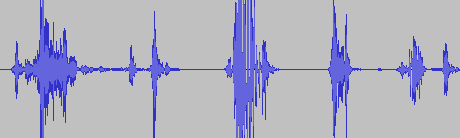
Stolen phone call audio from an infected device. Image: IBM.
Once ADB is established, the malicious PC or charger can reboot Nexus devices into the bootloader from where malware can be installed. On 6 devices, attackers can eavesdrop on communications including phone calls and SMS, while modem restrictions on the still current 6p model restrict attackers to stealing text messages.
"Furthermore, this level of access to the Nexus 6 modem allows attackers to find the exact GPS coordinates with detailed satellite information, place phone calls, steal call information and access or change nonvolatile items or the EFS partition," says Roee Hay and Michael Goberman of IBM's X-Force application security research team.
Five commands are used to enable the required USB options for attackers to have persistence on the devices which allows further now silent attacks to be made over a USB connection.
Attackers with a victim device in their hand can boot Nexus devices into fastboot and choose BP-Tools or Factory.
Another uninitialised kernel memory leakage bug (CVE-2016-6678) in Nexus 6 permits the theft of some network traffic.
"We also discovered a vulnerability in the f_usbnet driver itself in which four to five bytes of uninitialised kernel data are padded to every ethernet frame carried over USB," Hay and Goberman say. "This leak may contain sensitive data that could empower cybercriminals to exploit the system." ®
